theory behind linear momentum ball drop test|linear momentum and collisions pdf : purchasers Introduction. This lab seeks to confirm the conservation of linear momentum. We will give a steel ball an initial velocity by rolling it down a ramp. It will then collide with and become embedded in a wooden block. The momentum of the system before and after the collision will be compared. 11 de ago. de 2023 · Inscreva-se! O que é 9f Games? 9f games é confiável? Confira nossa análise do aplicativo em 2023! O 9f Games é um aplicativo com jogos de azar online, .
{plog:ftitle_list}
14 de dez. de 2018 · Enjoy the entire twentieth season of the PBS television series: Bob Ross - The Joy of Painting. #HappyTrees #ThankYouBob #OilPainting #BobRoss #TheJoyOfPainting
Introduction. This lab seeks to confirm the conservation of linear momentum. We will give a steel ball an initial velocity by rolling it down a ramp. It will then collide with and become embedded in a wooden block. The momentum of the system before and after the collision will be compared.One example of linear momentum conservation involves the recoil of a cannon (or a ri°e) when a shell is ̄red. A cannon of mass M = 3000 kg ̄res a shell of mass m = 30 kg in the horizontal .Linear momentum is defined as. p = mv. [kg⋅m/s] Momentum is a vector whose direction is the same as the velocity. So, in 2-D. px = mvx, py = mvy. Momentum is not the same as kinetic .Ball Drop Rebound Test. Hypothesis: What do you anticipate the result to be for ball return height? ________________ .
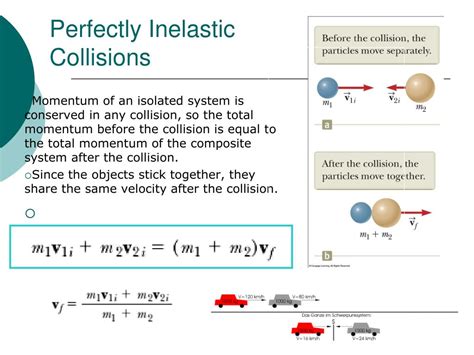
The total linear moment P is the vector sum of the individual particle’s linear momenta. The linear momentum of a system of particles is equal to the product of the total mass M of the system .Objective: llision between metal balls of unequal mass. To demonstrate the. Procedure: The instructor will demonstrate recording a collision with 60-Hz spark timers. Work with another .(In Albert Einstein’s Special Theory of Relativity, this nonrelativistic formula is altered, but the newly defined linear momentum is still conserved.) Why is total linear momentum .Problem statement: Suppose that a motion is described by the one-dimensional mapping, x 1 t X for t > 0. Determine (a) the velocities and accelerations in the spatial and material descriptions, .
Theory. The conservation of linear momentum (p = mv) is an important concept in physics. In a closed system, whenever momentum is conserved the initial and final total momentum are .The linear momentum of a particle is defined as the product of the mass of the particle times the velocity of that particle. Conservation of momentum of a particle is a property exhibited by any particle where the total amount of .For an object in linear motion, its momentum can be defined as . p=mv, or the momentum of an . Each pair should receive your approval for the surface they have chosen before conducting their drop test. 2 Next Gen STEM. . One student will hold the meter stick vertically on the surface and drop the ball from a height of one meter. b. The .In a previous part of Lesson 1, it was said that. In a collision, an object experiences a force for a given amount of time that results in its mass undergoing a change in velocity (i.e., that results in a momentum change).. There are .
linear momentum vs collision
The scientific definition of linear momentum is consistent with most people’s intuitive understanding of momentum: a large, fast-moving object has greater momentum than a smaller, slower object.. 8.1: Linear Momentum and Force - Physics LibreTexts
It's important to note that momentum is a vector quantity, meaning that the direction of the force is part of its definition; it's not enough to say an object has momentum, you have to say in which direction that momentum is acting. When Ball One hits Ball Two, it's traveling in a specific direction -- let's say east to west.Linear momentum is the momentum of an object that is moving in only one dimension; The linear momentum of an object remains constant unless the system is acted upon by an external resultant force; Momentum is defined as the product of mass and velocity; Where: = momentum, measured in kg m s −1 - mass, measured in kg = velocity, measured in m .
8. Estimate the uncertainty in the initial and final momentum. 9. Determine if momentum is conserved. If the initial and final values of momentum are not equal, examine the change in momentum as a percent of the magnitude of the average momentum based on the initial and final values calculated. p P P P f P i; % P 100s) Q8. Two speedboats are moving at constant speeds on a straight stretch of a racecourse. At the instant shown, Speedboat A has more momentum thanPhysics 207 - Lab 5 - Linear Momentum Introduction This lab seeks to confirm the conservation of linear momentum. We will give a steel ball an initial velocity by rolling it down a ramp. It will then collide with and become embedded in a wooden block. The momentum of the system before and after the collision will be compared. Measure the ball's .3-D rendering of the cradle in motion. Newton's cradle is a device, usually made of metal, that demonstrates the principles of conservation of momentum and conservation of energy in physics with swinging spheres.When one sphere at the end is lifted and released, it strikes the stationary spheres, compressing them and thereby transmitting a pressure wave through the stationary .
linear momentum lab questions
Figure 1. a car of mass m1 moving with a velocity of v 1 bumps into another car of mass m 2 and velocity v 2 that it is following. As a result, the first car slows down to a velocity of v′ 1 and the second speeds up to a velocity of v′ 2.The momentum of each car is changed, but the total momentum ptot of the two cars is the same before and after the collision (if you assume .
In a previous part of Lesson 1, it was said that. In a collision, an object experiences a force for a given amount of time that results in its mass undergoing a change in velocity (i.e., that results in a momentum change).. There are four physical quantities mentioned in the above statement - force, time, mass, and velocity change.Secondly: momentum is only conserved for a system in the absence of any external force. if you treat the ball as your system, the force exerted by the wall on the ball constitutes an external force for this system, and thus conservation of momentum for the ball simply does not apply. What if you consider the ball plus wall as the system?
豆類 水分計
Figure 5.29 (a) We analyze two-dimensional projectile motion by breaking it into two independent one-dimensional motions along the vertical and horizontal axes. (b) The horizontal motion is simple, because a x = 0 a x = 0 and v x v x is thus constant. (c) The velocity in the vertical direction begins to decrease as the object rises; at its highest point, the vertical .This video tutorial lesson explains how an impulse changes an object's momentum. Attention is given to what an impulse is and how it can be mathematically related to momentum change in order to understand collisions? Mr. H explains the important connection between impulse and momentum and explains how to use the idea..
Momentum as a Vector Quantity. Momentum is a vector quantity.As discussed in an earlier unit, a vector quantity is a quantity that is fully described by both magnitude and direction. To fully describe the momentum of a 5-kg bowling ball moving westward at 2 m/s, you must include information about both the magnitude and the direction of the bowling ball.For particles moving with speeds far smaller than the speed of light c, the linear momen-tum is simply the product of the particle’s mass and its velocity. ~p = m~v (In Albert Einstein’s Special Theory of Relativity, this nonrelativistic formula is altered, but the newly defined linear momentum is still conserved.)Bouncing Ball Physics Bouncing ball physics is an interesting subject of analysis, demonstrating several interesting dynamics principles related to acceleration, momentum, and energy. These principles will be discussed. Almost everybody, at some point in their lives, has bounced a rubber ball against the wall or floor and observed its motion.
Investigate simple collisions in 1D and more complex collisions in 2D. Experiment with the number of balls, masses, and initial conditions. Vary the elasticity and see how the total momentum and kinetic energy change during collisions.Ball Drop Rebound Test . Hypothesis: What do you anticipate the result to be for ball return height? _____ _____ Drop the golf ball, the same way, for all five trials. For each trial, the measurer should tell the recorder the rebound height of the first bounce. After your group has completed five trials for the golf ball, calculate the average .drop, and radiated energy. Theoretical Formulation The equations outlined below describe a mathematical framework for representing seismic signals based on the as-sumptions of linear transfer functions or linear systems theory (e.g., Hsu and Breckenridge, 1981; Oppenheim et al., 1983). Throughout this article, we denote convolution in time by ⊗,
linear momentum lab answer key
In the previous calculation, performed in the frame where clay ball #2 was stationary (often referred to as the laboratory frame), the system still has the same rest frame energy (this quantity, like internal energy for collections of particles, is intrinsic to the system), and since all of this is converted into thermal energy, we see the . Based on Momentum Transfer from a Ball Drop by Gregory C. McLaskey , * David A. Lockner, Brian D. Kilgore, and Nicholas M. Beeler Abstract W e describe a technique to estimate the seismic moment .
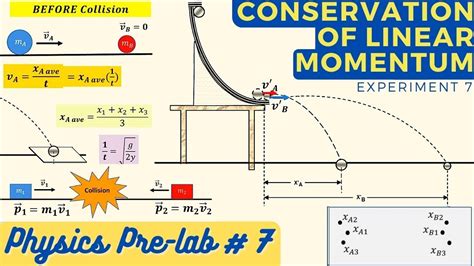
Experiment V: Conservation of Linear Momentum Goals . You may test it by running the projectile ball over the screw without the target ball on top. Now place the other steel ball on the support screw and roll the projectile ball down the chute to produce a collision. Record the landing positions of the two balls by using twoMomentum is found to be a property of all subatomic particles including massless particles such as photons that compose light. Momentum being a property of particles hints that momentum may have an identity beyond the description of an object’s mass multiplied by the object’s velocity. The Egg Drop is a classic science class experiment for middle school or high school students. Students are given an egg to drop from a high point (such as the roof of the school) onto a hard surface (such as the parking lot). They must design a carrier for the egg to house it during the drop. Typical carriers are milk cartons or shoeboxes.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A rubber ball and a lump of clay have equal mass. They are thrown with equal speed against a wall. The ball bounces back with nearly the same speed with which it hit. The clay sticks to the wall. Which one of these objects experiences the greater momentum change? A. the ball B. the clay C. Both of them .
linear momentum formula
linear momentum definition
linear momentum and collisions pdf
WEBLike never before, download every Playboy issue ever published, from the very first issue of December 1953 featuring Marilyn Monroe to the latest issue of 2022, over 1800 digital .
theory behind linear momentum ball drop test|linear momentum and collisions pdf